LINEAR SLIDES
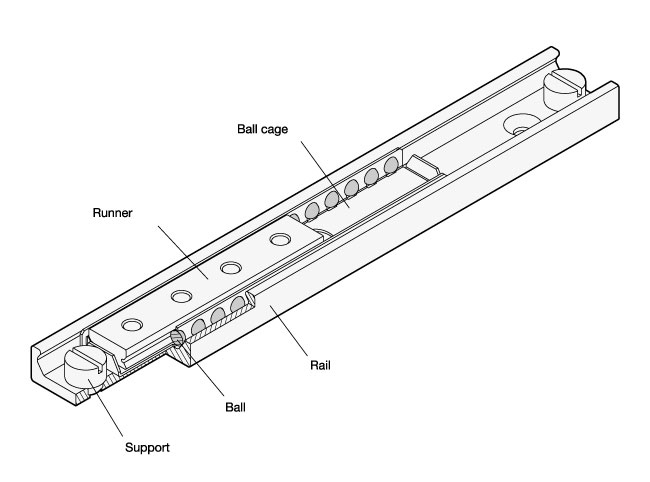
All linear slides consist of an outer rail with a runner moving inside. Anti-friction bearings, kept at a distance and in position by means of a ball cage, lie between the rail and the runner.
Rail and runner are made of heat treatable steel, enabling their use in industrial environments with higher requirements in terms of load rating, quiet operation and useful service life.
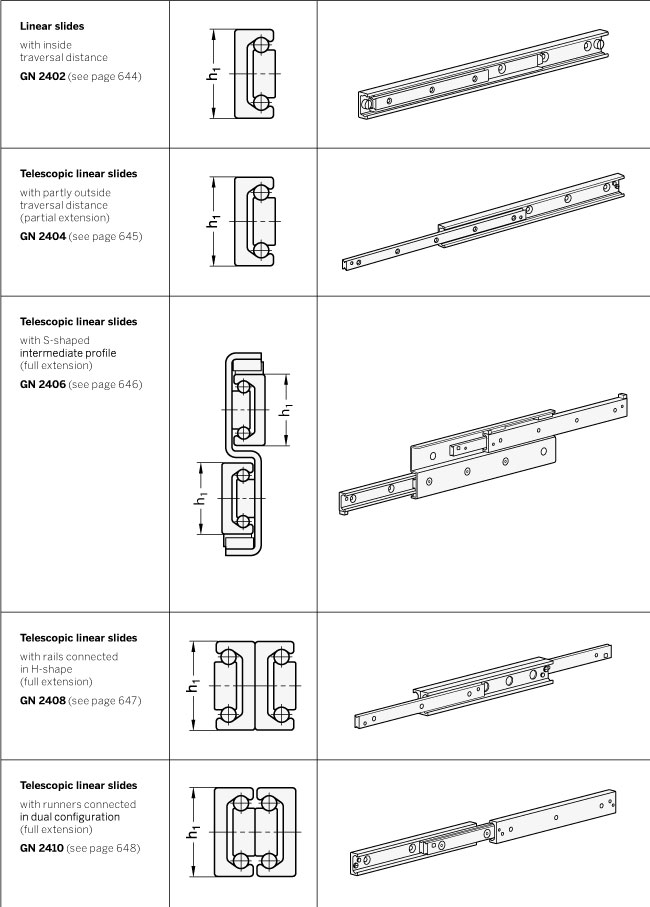
All designs are available in the nominal rail dimensions h1 = 28, 35 and 43 mm and may also be supplied beyond the standard range in lengths from 130 mm to 1970 mm, appropriate for individual requirements.
Linear slides are normally adjusted so that a clearance-free (i.e. moderately pre-stressed) match-up is created between rail and runner. The raceways of the rails and runners are induction hardened, which combined with the antifriction bearings results in lower wear and longer service life. Linear slides are permanently lubricated with a high-grade special grease designed for linear guide rail systems.
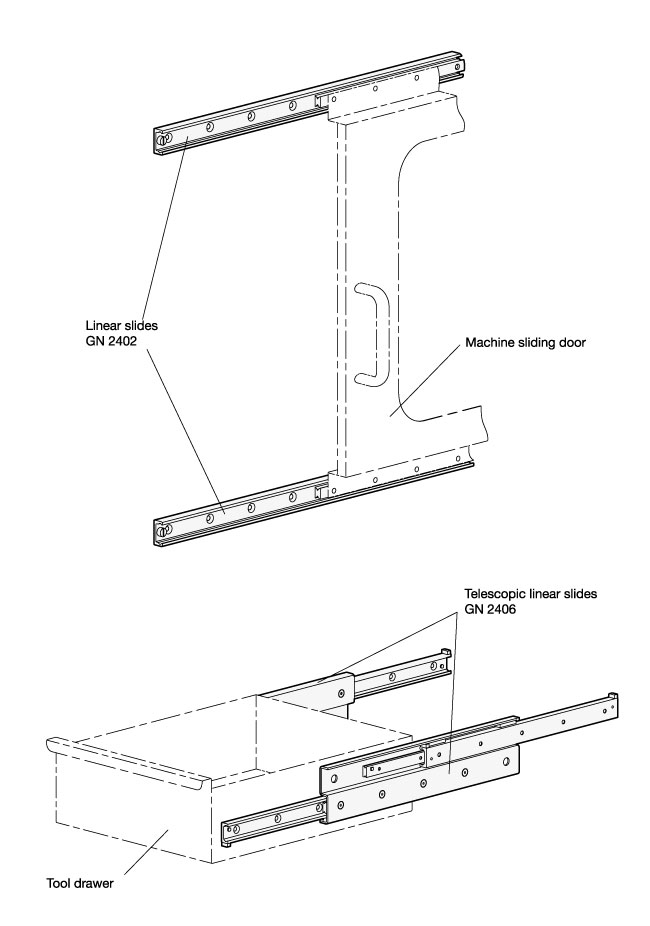
Depending on requirements, a variety of different types are available. Sliding distances of the runners are inside, partly outside or entirely outside the length of the rails. Fully extendable telescopic linear slides consist of linear slides directly interconnected at the rails, the runners or with the help of an intermediate profile.
To mount linear slides, countersinks in the rails and, depending on type of construction, threaded or countersunk holes in the runners are available. The compact style is generally advantageous for use in tight spaces.
-
Generals
-
1. Plastic materials
- 1.1 Mechanical strength
- 1.2 Thermal resistance
- 1.3 Strength and surface hardness
- 1.4 Resistance to chemical agents
- 1.5 Resistance to atmospheric agents and uv rays
- 1.6 Flame resistance
- 1.7 Electrical properties
- 1.8 Surface finish and cleanability
- 1.9 Compliance with international standards
- 1.10 Competence of Elesa+Ganter technical department
- 2. Metal materials
- 3. Other materials
- 4. Machining tolerances
- 5. Fixed handles
- 6. Assembly measures
- 7. Special executions
- 8. Colours
- 9. Test values
-
10. Technical tables
- 10.1 Conversion tables
- 10.2 DIN 79 Square holes and shafts
- 10.3 DIN 6885 Keyways
- 10.4 GN 110 and GN 110.1 Transversal holes
- 10.5 DIN 13 ISO Metric threads
- 10.6 DIN 228 Cylindrical GAS-BSP threads
- 10.7 DIN EN ISO 898-1 | DIN EN 20898-2 Strenght values
- 10.8 DIN ISO 286 ISO-Fundamental tolerances
- 10.9 IP Protection Classification
- 10.10.1 PFB | PRB Thread locking with jamming action Polyamide patch coating/ Polyamide complete coating
- 10.10.2 MVK Thread locking gluing Micro encapsulation precote 80 (red)
- 10.11 Stainless Steel characteristics
- 10.12 Surface treatments
- 10.13 Carbon steel, zinc alloys, aluminium, brass characteristics
- 10.14.1 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics
- 10.14.2 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics
- 10.14.3 Duroplast, elastomer, technopolymer and rubber characteristics
- 10.15 Load ratings U-Handles
- 10.16 Load ratings metal hinges
- 10.17 Strength of indexing plungers
- 10.18 Assembly sets GN 965 and GN 968
- 11. Vibration-damping elements
-
1. Plastic materials
- Hygienic design
- Operating Elements
- Clamping knobs
- Control elements
- Rotary controls
- Indexing elements
- Joints
- Transmission elements
- Levelling elements
- Hinges
- Latches
- Toggle, power and hook clamps
- Accessories for hydraulic systems
- Tube clamp connectors
- Castors and wheels
- Magnets
- Conveyor components
- Linear slides
- Vibration mounts
- Vacuum components
- Elastomer springs